Living with diabetes can feel like navigating a minefield, especially when it comes to unexpected guests like yeast infections. If you’ve ever experienced that itchy, uncomfortable rash, you’re not alone. It’s a common issue for many, and understanding what you’re dealing with is half the battle.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Diabetic Yeast Infections
Diabetic individuals are prone to yeast infections due to elevated blood sugar levels. Understanding the causes and symptoms can aid in effective management.
Causes of Yeast Infections in Diabetics
High glucose levels promote yeast growth. The Candida fungus thrives in warm, moist environments, which often occur in areas such as skin folds. Poor blood circulation, a common issue in diabetes, can lead to skin breakdown, further increasing susceptibility. Additionally, antibiotic use disrupts the natural balance of flora, allowing yeast to flourish. Maintaining optimal blood sugar control significantly reduces the risk of infections.
Symptoms of Yeast Infections
Common symptoms include itching, redness, and swelling in affected areas. Discomfort often intensifies during wearing clothing or movement. Skin may appear flaky or develop a rash, indicating irritation. Additionally, a thick, white discharge from affected areas may occur in women. Early recognition of these signs enables quicker treatment, minimizing discomfort and complications. Handling symptoms promptly contributes to overall better health management in diabetics.
Identifying the Rash
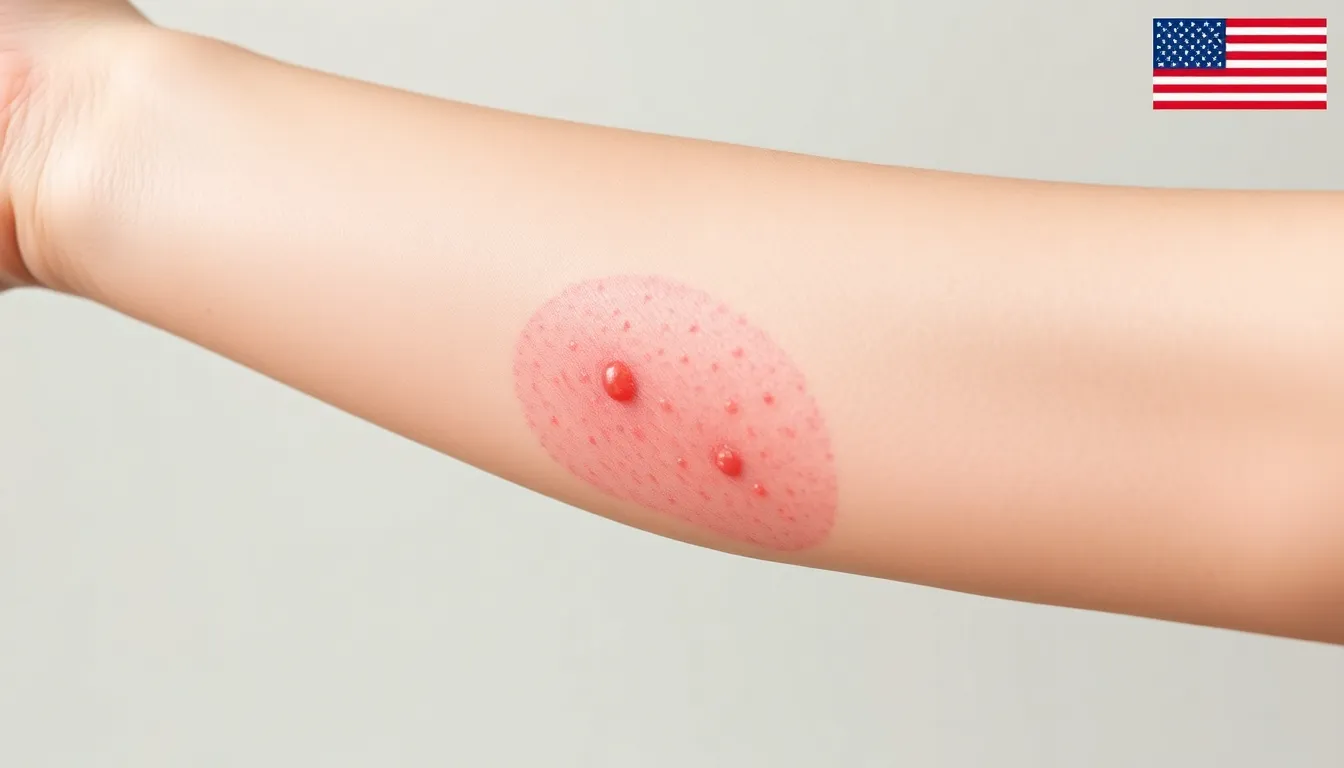
Recognizing a diabetic yeast infection rash involves awareness of its distinct traits. Symptoms can vary but often include itching and irritation in specific areas.
Common Characteristics of the Rash
Redness and swelling typically appear around the affected area. Itching often intensifies, especially in warm, moist environments. Many experience discomfort during movement or while wearing clothing. A rash might also present small bumps or blisters, contributing to irritation. Odor may develop due to the yeast’s activity, signaling the presence of an infection.
Variations in Rash Appearance
Rashes can differ significantly in appearance based on individual factors. Some may display a bright red color, while others could appear more subdued. The texture can vary from smooth to scaly, affecting how it feels against the skin. In some cases, the rash may form crusts or peeling skin, indicating an advanced stage. Visual differences often reflect the severity of the infection and its response to treatment.
Diabetic Yeast Infection Rash Pictures
Diabetic yeast infections can manifest visually, with rashes often characteristic of this condition. Viewing images plays a crucial role in identifying and understanding these rashes.
Reference Images for Better Understanding
Various reference images showcase the differing presentations of diabetic yeast infection rashes. Some pictures depict bright red rashes accompanied by swelling, while others illustrate subdued, scaly patches. Additional images may highlight areas where irritation is most prominent, emphasizing the importance of recognizing specific traits. Viewing these visuals helps individuals better understand the condition’s appearance and its potential variations.
Descriptions Accompanying Each Image
Descriptions accompanying each image clarify the features of diabetic yeast infection rashes. An image showing a bright red rash might highlight the intensity of itching and discomfort experienced by individuals. Another image may focus on scaly textures and small bumps, indicating a more advanced stage of infection. Observations about the presence of odor or crusting may accompany certain visuals, portraying the severity of symptoms. Such detailed descriptions enhance the viewer’s understanding of what to look for when assessing potential infections.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for diabetic yeast infections can involve several approaches. Managing symptoms promptly is essential for comfort and overall health.
Medical Treatments
Doctors often recommend antifungal medications to address yeast infections. These prescriptions might include topical creams, such as clotrimazole or miconazole. Oral options, like fluconazole, can also provide effective relief. Physicians may suggest lifestyle modifications alongside medication, including tighter blood sugar control to prevent recurrence. Continuous monitoring of symptoms helps identify if treatments are effective or if adjustments are necessary.
Home Remedies
Many individuals turn to home remedies for relief from mild symptoms. Yogurt containing live cultures can restore healthy bacteria and combat yeast growth. Applying coconut oil typically creates a barrier that prevents moisture buildup. Some people find oatmeal baths soothing for irritated skin, as this can alleviate itching and discomfort. Staying dry and wearing breathable fabrics are practical preventive measures that can significantly reduce infection risk.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing diabetic yeast infections involves strategic lifestyle choices. Implementing effective dietary changes and maintaining proper hygiene significantly lowers the risk of infection.
Dietary Changes
Choosing a balanced diet plays a vital role in managing diabetes and reducing yeast infection risks. Prioritizing foods low in sugar helps keep blood glucose levels stable. Incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of vegetables supports overall health. Including probiotics, such as yogurt or kefir, promotes healthy gut bacteria, which can combat yeast overgrowth. Limiting processed foods and refined carbohydrates also minimizes spikes in blood sugar. Hydration should not be overlooked; drinking adequate water helps flush out excess glucose. Ensuring a consistent eating schedule stabilizes energy levels, ultimately benefiting blood sugar control.
Hygiene Practices
Practicing good hygiene provides essential protection against yeast infections. Regular showering helps eliminate sweat and moisture, especially in warm areas of the body. Wearing breathable fabrics, like cotton, promotes air circulation and keeps skin dry. Changing out of wet clothing promptly is crucial for preventing bacterial growth. Ensuring skin is completely dry after washing, particularly in skin folds, reduces infection risk. Avoiding irritants, such as harsh soaps, further protects sensitive areas. Regularly examining the skin for any signs of irritation or rash allows for early intervention and effective management.
Understanding diabetic yeast infections is vital for effective management and prevention. Recognizing the distinct characteristics of these rashes can empower individuals to seek timely treatment and alleviate discomfort. By staying informed about symptoms and treatment options, those living with diabetes can take proactive steps to maintain their health.
Incorporating lifestyle changes and good hygiene practices plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of infections. With the right knowledge and approach, managing the challenges of diabetes, including yeast infections, becomes more manageable, leading to improved quality of life.



